Introduction
For the past almost 30 years since the inception of computer graphical user interface (GUI), the traditional way humans interacting with computer applications has been through screen navigation by scrolling up and down, clicking buttons, menu options, links and icons etc. The pain points of the traditional human-computer interaction are that traditional search function always provides numerous search results. Users have to spend time choosing the results. Moreover, if the users overlook some content displayed on the screen, users would think the information doesn’t exist.
Since the emergence of the Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Model (LLM) in the consumer market in November 2022, we are witnessing a paradigm shift in human-computer interaction, moving from the tradition user interfaces (UI’s) to conversation powered interfaces represented by an AI Chatbot appearing on the side of the screen. This transition from user interface to chat interface is revolutionising user experiences and unlocking new capabilities. The search results are a lot narrower and sometimes the users are presented with a single result.
The Rise of AI Chatbot
A few years before the arrival of GenAI and LLM, chat interfaces already gained tremendous popularity through the rise of chatbots, voice assistants. In the past almost a year, the AI-powered conversational agents have added more sophisticated features to “converse” with the users both in spoken and written human languages.
GenAI and LLM are further advancing the natural language processing and speech recognition capability to enable machines to understand nuanced human language and generate fluent, conversational responses. Chat interfaces leverage these capabilities to provide intuitive experiences. The Chat Interface represents the culmination of conversational AI coming of age which is quickly becoming the prevailing human-machine interface of the moment with more and more organisations are adopting the AI Chatbot in both their internal applications and external pages. Rather than manipulating GUI elements, users simply conduct natural conversations to interact with systems and accomplish tasks through the Co-pilot, a form of AI Chatbot designed to assist users in conducting administrative tasks.
Leading AI Chatbots can handle multi-turn conversations spanning complex topics and tasks. The integration with backend systems allows the AI Chatbots to actually complete tasks such as booking annual leaves for employees or placing orders for customers rather just answering questions.
The AI Chatbots effectively act as an intelligent interface layer, translating natural human conversations into structured data to drive actions across the organisation. These AI agents are central to delivering the benefits of intuitive, conversational user experiences.
Benefits over Traditional User Interfaces
Chat interfaces provide significant advantages over traditional UI’s that rely on typing, tapping and swiping. Some key benefits include:
Natural Interaction
Having a conversation comes instinctively to humans. Chat interfaces build on this natural mode of interaction. Users don’t have to learn and recall complicated menu hierarchies, multi-step processes or command syntax.
Hands Free Control
Voice-based chat interfaces enable hands free control, allowing users to multitask and be more productive. This makes them ideal for situations where screens are inaccessible
Personalisation
Unlike rigid menus and buttons, conversations are dynamic and adaptive. Chat interfaces leverage AI to understand user intent, context and preferences to provide personalised responses and suggestions.
Navigation Free
Convenience Chat eliminates the need for switching between apps to complete tasks. Users can access features, ask questions, lookup information and executive transactions all within one conversation.
Speed Chat
Speed Chat is often the fastest way to get something done, rather than hunting through complex apps and menus. Voice input can be up to three times faster than typing on the keyboard or tapping on mobile phone screen.
Road Map to implement AI Chatbot effectively and successfully
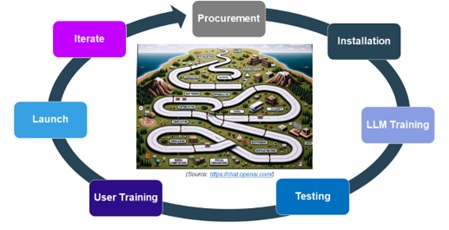
To successfully utilise the AI Chatbot to improve user experience as listed above in this article, organisations must adopt a roadmap to adopt the AI Chatbots. These steps require a phased approach spanning procurement, installation, customisation, testing, training, launch and continuous improvement:
Procurement
First, leading the GenAI platforms should be evaluated and selected based on the use cases, accuracy, data considerations and other requirements compared against the capabilities of the GenAI products.
Installation
The next step is to ensure whether the chosen platform is installed on-premises or in the cloud, it should be compatible to be integrated with existing infrastructure. Care should be taken to ensure proper access controls and security protections are in place.
Training
A key step is then further training and fine-tuning the base model on the airport operator’s proprietary data to customise it to internal content styles, terminology, and formats. Subject matter experts should inform the datasets used. Identify high frequency tasks that involve multiple steps and menu navigation – these yield maximum productivity gains from conversation interfaces. Below are some recommendations for consideration:
- Build agents iteratively using feedback loops with real users, avoiding over automation. Human-in-the-loop conversations can train AI models
- Leverage pre-built platforms with robust natural language processing (NLP) and speech recognition capabilities to accelerate development
- Design conversations to be natural and contextual rather than rigid command driven interactions
- Start with text-based over voice to minimise errors. Expand to voice interface with ubiquitous usage
- User personas, dialogue samples and content libraries to easily scale interface to cover diverse users and tasks
Testing
Extensive testing must validate the AI Chatbot’s output quality before being presented to users. Both technical and business stakeholders should review results across diverse sample inputs and use cases.
User Training
Comprehensive training should be conducted with end users on how to apply and interact with the models through AI Chatbot and Co-pilot interfaces. Education on topics like prompt engineering, AI ethics and cybersecurity is crucial.
Launch
After launching the AI Chatbots, user feedback loops need to be put in place to continue model refinement and improve performance through ongoing machine learning. Data sources and use cases can also be expanded over time to extend capabilities.
Iterate
Bringing AI Chatbots into production requires thoughtful orchestration across technology implementation, customisation, testing, training, adoption and iteration. This staged approach can ensure the AI Chatbots achieve maximum business impact to improve user experience.
Conclusion
With the GenAI and LLM capabilities, AI Chat interfaces have become viable for real world applications. As the technology continues to improve, we can expect chat interfaces become pervasive across devices, platforms and industries. The next frontier is multimodal chat leaping beyond text and voice to visualisation. For instance, with the inclusion of camera in the chat interface, the AI Chat assistants could understand user’s gestures, eye movements and emotions during the conversations to enable richer engagement. Chat interfaces could also augment virtual worlds in the metaverse. Instead of learning how machines work, machines are now learning how best to communication with humans and this conversational interfaces will continue to evolve further.
About the author:
Dr Kitty Hung, a BCS Fellow, has over 24 years of experience in the IT sector as a business and system analyst, project manager and technologist covering policing, national security, telecommunications, critical national infrastructure, defence, transportation, disruptive & emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Digital Twin. She is currently a Principal Consultant with AtkinsRéalis (www.atkinsrealis.com) focusing on the development and the adoption of Generative AI technology. Kitty is an experienced and passionate mentor, coach, public speaker, volunteer and charity fundraiser to help others and to give back to the community.
LinkedIn Profile:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/kitty-hung-phd-citp-bcs-fellow-03120a66/